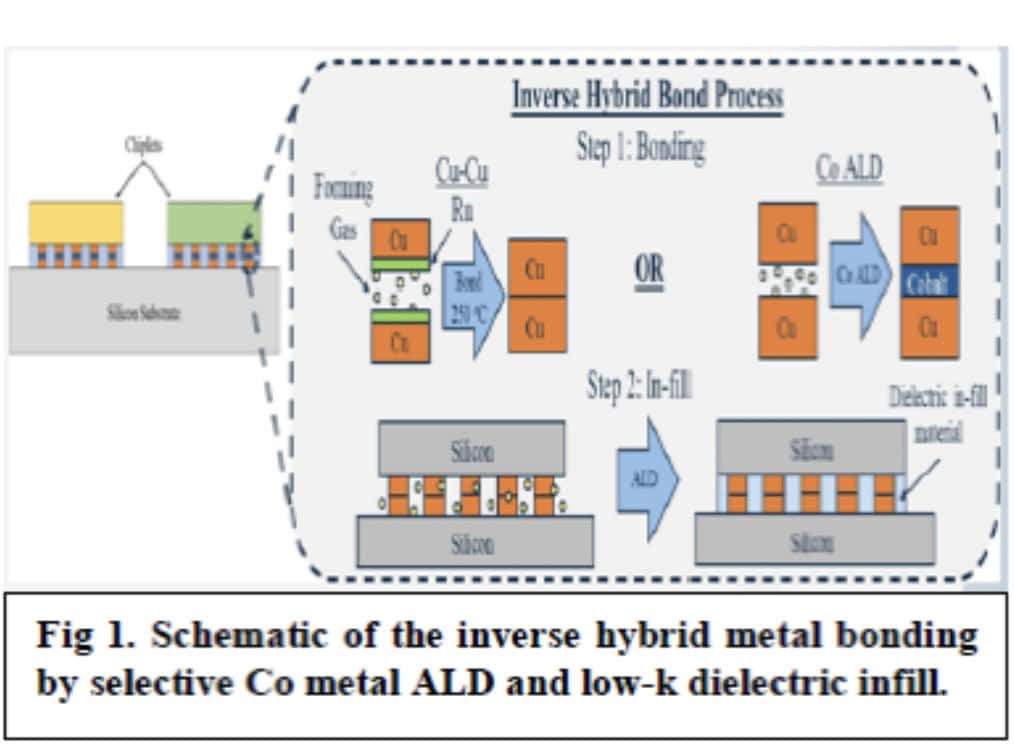
Increased interconnect density is being driven by AI and High Performance Computing (HPC) applications. Inverse Hybrid Bonding is one of the 3D bonding techniques being investigated to achieve ultra-dense I/O interconnects. The use of selective Co ALD along with a cyclic clean was explored as a method to bond the Cu pads of two substrates.
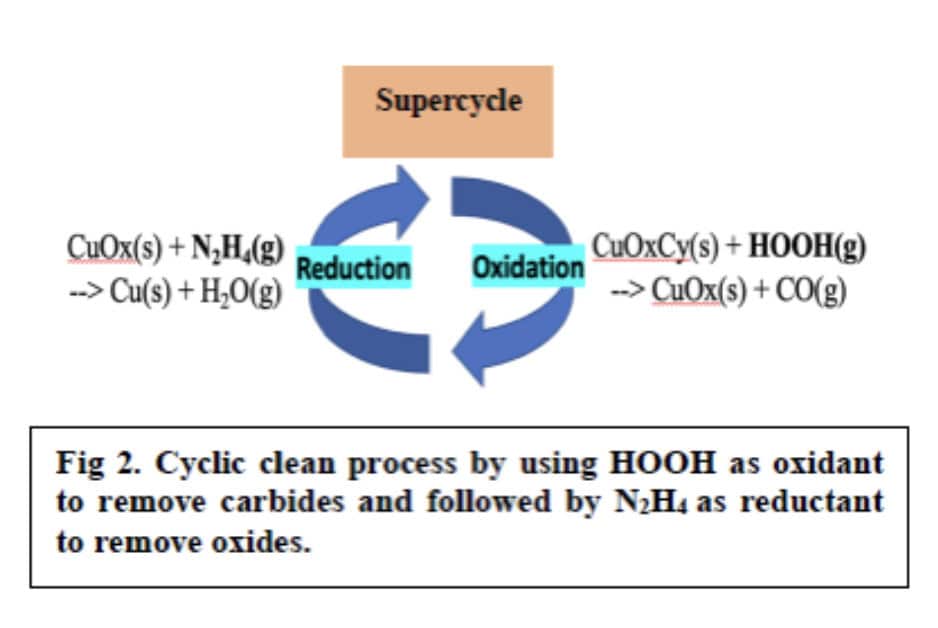
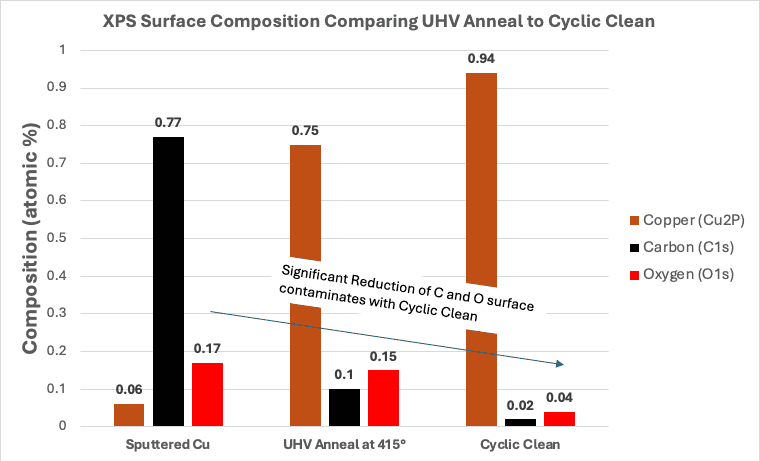
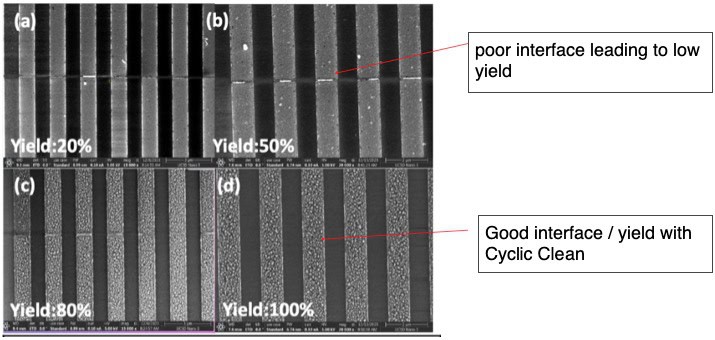
This work, performed at UCSD, studied the use of a Hydrogen Peroxide (HOOH) and Hydrazine (N2H4) vapors produced by RASIRC to improve dramatically the connection yield of Cu/Co/Cu test structures. The cyclic clean process, using HOOH and N2H4, was performed at 340 °C. In the cyclic cleaning process, the HOOH vapor was first introduced to oxidize the carbide contaminates, followed by Hydrazine vapor to reduce the oxides. This approach resulted in a significantly lower C and O surface contamination on Cu surface compared to conventional UHV high-temperature annealing (415 °C), prior to selective Co deposition.